|
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Tracers
Tracer is a detectable
substance added to a chemical, biological, physical or industrial system
by means of some injection or labelling technique in order to study and
evaluate the characteristics and the dynamic behaviour of such a process. Examples of tracers are solids in
suspension, dyes, salts, alcohols and radioisotopes. The major advantage
of radiotracers is that they can be detected without physical contact and
therefore without affecting the system. The selection of the most suitable tracer for a given process is extremely important. In any case it should satisfy the following conditions:
In case of using radiotracers, they must also satisfy conditions regarding the type and energy of the emitted radiation and their half-life. On the other hand they have the following advantages:
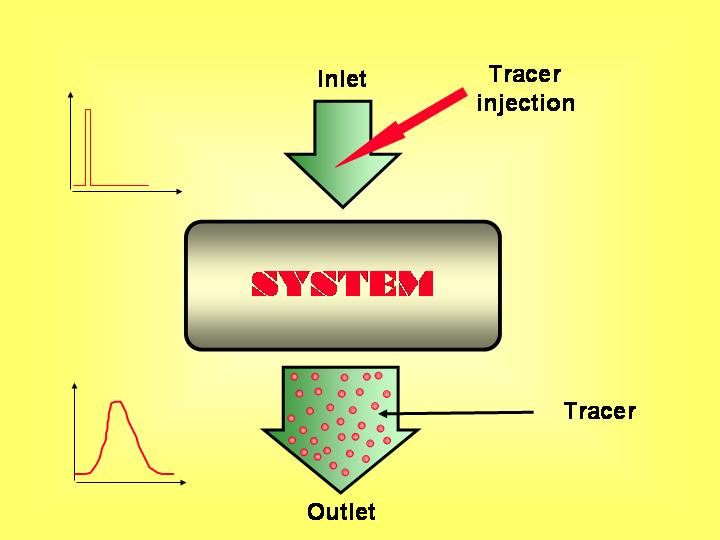
Applications Using radiotracers makes it possible to analyse the behaviour of almost any industrial process and therefore easy the detection of died volumes, multiple transport paths of materials, internal recycling and many other malfunctions that may affect the normal operation of the system. Leak detection, velocity and flow rate measurement, mass balance and mixing efficiency are some of the better well known radiotracer applications in industrial processes. Residence time distribution Radiotracers are the best tool whenever the knowledge of residence time distribution (RTD) in an industrial process is needed. As a matter of fact the system response at an instantaneous tracer injection is precisely the RTD function of this system. The system response is the concentration as a function of time curve in its outlet. In the simplest case the knowledge of the mean residence time and its standard deviation is enough information to evaluate the process but in more complex systems it is preferred to analyse their transfer function in detail, to evaluate all the statistic parameters and to apply mathematical models. These models allow the engineers to decompose the process in a set of interconnected simple systems. Then the model can be "tuned" modifying some of its parameters aiming to the optimisation of the process and the further increase in the production efficiency. More information ...
|